Introduction
Biomolecular Engineering Laboratory
Professor
Sun-Gu Lee
Members
· Selvakumar Edwardraja
· Nagasundarapandian Soundrarajan
· Govindan Ragunathan
· Sriram Sokalingam
· Heo Mi Ae
· Nagasundarapandian Soundrarajan
· Govindan Ragunathan
· Sriram Sokalingam
· Heo Mi Ae
Research Interests
Protein is a polymeric molecule made of twenty amino acids, which forms an original three-dimensional structure depending on its amino acid sequence. Since the folded proteins act directly as enzymes, antibodies and so on in a cell, we can use them as functional molecules in various biological and non-biological systems. However, the physical properties of natural proteins such as stability, activity and solubility are limited to the range of natural environmental condition because they have been evolved through natural pathways.
Protein engineering focuses on the overcoming of the limitations and the improvement of the physical properties of the natural proteins. Various protein engineering principles and methods including computational design, directed evolution, and genetic code engineering have been developed so far, which permit us to engineer proteins successfully, but partly. Our aim is to find out new protein engineering principles which can be more generally employed in the design of proteins showing unnatural physical properties
Protein engineering focuses on the overcoming of the limitations and the improvement of the physical properties of the natural proteins. Various protein engineering principles and methods including computational design, directed evolution, and genetic code engineering have been developed so far, which permit us to engineer proteins successfully, but partly. Our aim is to find out new protein engineering principles which can be more generally employed in the design of proteins showing unnatural physical properties
Recent Research
1.One of the drawbacks in the modification of ScFv is that its use in the field of medicine and diagnosis is limited due to the absence of method for the large-scale production of site-specifically modified ScFv. Here we attempt to design an active and soluble ScFv in a reducing condition as well as to develop a biological and site-specific method to introduce unnatural chemical groups into ScFv on large scale.
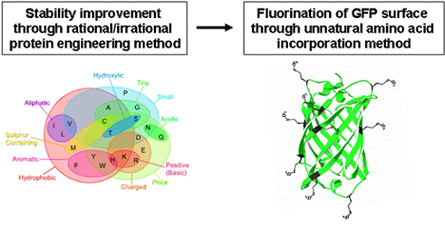
2.One of the drawbacks in the use of GFP is that its use is limited to aqueous system due to its hydrophilicity, a natural property of protein. In hydrophobic non-aqueous system, the stability and solubility of GFP are very low, which causes many problems. The objective of this research is to confer stability and solubility to GFP in non-aqueous system such as organic solvents by engineering GFP through various protein engineering methods and to characterize the engineered GFP in order to expand the applicability of GFP to non-aqueous system.
2.One of the drawbacks in the use of GFP is that its use is limited to aqueous system due to its hydrophilicity, a natural property of protein. In hydrophobic non-aqueous system, the stability and solubility of GFP are very low, which causes many problems. The objective of this research is to confer stability and solubility to GFP in non-aqueous system such as organic solvents by engineering GFP through various protein engineering methods and to characterize the engineered GFP in order to expand the applicability of GFP to non-aqueous system.
 Chemical & Biomolecular Engineering
Chemical & Biomolecular Engineering